HBM Technology Leads the AI Era: Selection and Procurement Guide
In 2025, the global memory market is undergoing a disruptive transformation driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and High-Performance Computing (HPC). Traditional memory products, such as DDR5, while continuously iterating, face increasing bandwidth bottlenecks when confronted with the growing scale of AI models and computational demands. The need for data throughput in AI servers, data center accelerators, and edge computing devices has reached an unprecedented level—it's not just a quantitative increase, but a qualitative requirement for memory architecture.
High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) is the core technology in this transformation. According to market forecasts, HBM's market share and growth rate will continue to outpace traditional DRAM.
Leading AI accelerators, such as the NVIDIA B200 chip, have adopted HBM as their sole memory configuration, underscoring the GPU's absolute reliance on HBM's extremely high bandwidth. HBM has evolved from a high-end "luxury item" to the core infrastructure of the AI era.
Why is HBM so popular, becoming the key to the AI compute race? This article will delve into HBM's technical principles, analyze how it solves the core pain points of AI workloads, and provide a practical guide for HBM selection and procurement.
What is HBM? Why Do We Need It?
HBM (High Bandwidth Memory) is a high-performance memory solution whose core innovation lies in the adoption of 3D Stacking technology. It uses Through Silicon Via (TSV) technology to vertically stack multiple DRAM dies, connecting them to the host chip (such as a GPU/ASIC) with an extremely wide bus width (typically 1024-bit or 2048-bit).
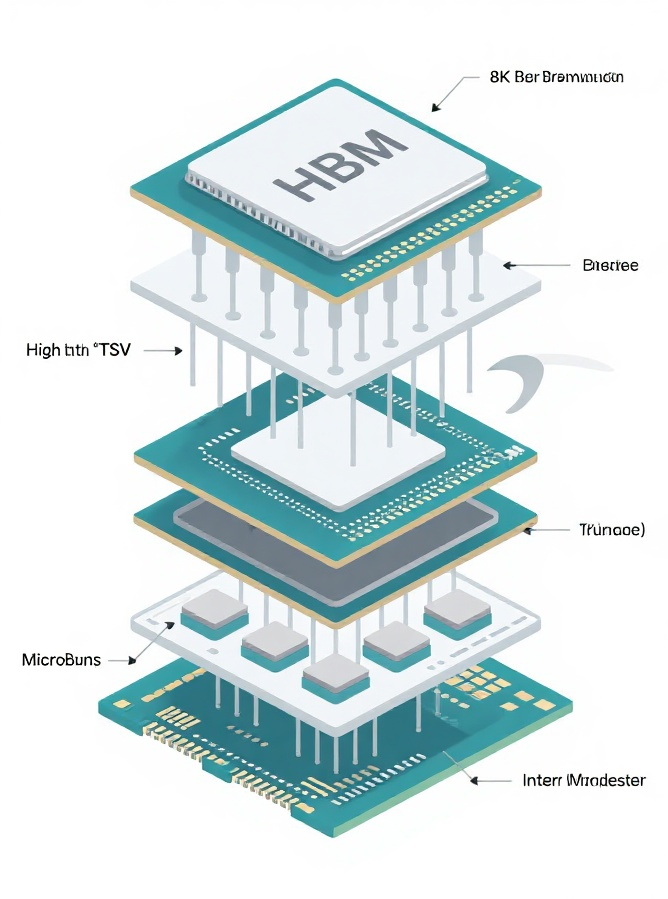
Architectural Comparison:
HBM differs significantly from traditional memory (DDR) and graphics memory (GDDR) in its design philosophy; it is specifically engineered to overcome the "bandwidth wall."
| Feature | DDR (e.g., DDR5) | GDDR (e.g., GDDR7) | HBM (e.g., HBM3e) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Application | General Servers/PCs | Graphics Cards/Gaming | AI Accelerators/HPC |
| Bandwidth | Relatively Low (~100 GB/s) | High (~1 TB/s) | Extremely High (>1.5 TB/s) |
| Bus Width | Narrow (64/128-bit) | Wide (256/384-bit) | Ultra-Wide (1024/2048-bit) |
| Latency | Low | Medium | Medium-High |
| Power Efficiency | General | Higher | Extremely High (Per bit) |
| Packaging/Integration | DIMM Slot | Discrete chip (on board) | 2.5D/3D Packaging (CoWoS, etc.) |
HBM's Key Advantage: It sacrifices minor latency for an exponential increase in bandwidth and superior power efficiency, a perfect fit for the demands of AI training.
Technology Evolution
HBM technology is evolving rapidly, with each generation bringing significant breakthroughs in bandwidth and capacity:
| Generation | Key Technical Breakthrough | Typical Bandwidth (Pin Speed) | Typical Total Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|
| HBM2/HBM2e | Introduced TSV stacking, significant bandwidth increase | 2.4 - 3.2 Gbps | ~410 GB/s |
| HBM3 | Capacity and speed leap, higher stacking | 5.6 - 6.4 Gbps | ~819 GB/s |
| HBM3e | Further speed increase, standard for mainstream AI chips | 8 Gbps and above | >1.2 TB/s |
| HBM4 (Outlook) | Higher stack layers (16Hi), further speed increase | To be determined | Projected > 2 TB/s |
How Does AI "Exhaust" Traditional Memory?
AI Server Pain Points
With the development of Large Language Models (LLMs) and multimodal models, AI training poses two major challenges for memory:
- Bandwidth Thirst (The I/O Wall):
Code Block Example: The backpropagation and gradient update processes in models require the GPU/accelerator to read and write trillions of bytes of data in an extremely short time.
# Simulate data movement bottleneck in AI training # Assume a Tensor size of 1TB, needs to be transferred N times per second Data_Size_TB = 1 Required_Bandwidth_TBps = Data_Size_TB * Iterations_Per_Second * 2 # Read + Write # Traditional DDR5 (Assume total bandwidth 0.4 TB/s) vs HBM3e (Assume total bandwidth 1.2 TB/s) if Required_Bandwidth_TBps > 0.4 and Required_Bandwidth_TBps <= 1.2: print("DDR5 becomes the bottleneck, HBM3e can meet the demand.")
The bandwidth of traditional memory severely limits the computational power of the GPU/accelerator. - Power Consumption Challenge: As the TDP (Thermal Design Power) of AI chips continues to climb, memory must also pursue higher power efficiency to maintain the overall sustainability of data centers.
HBM's Solution
HBM's design perfectly addresses the pain points of AI accelerators:
- Bandwidth Advantage: HBM's ultra-wide bus width (1024-bit and above), combined with high Pin Speed, easily achieves ultra-high bandwidth at the Tb/s level, completely breaking the "I/O Wall."
- Physical Integration: Through advanced packaging technologies like CoWoS, HBM is placed in close proximity to the accelerator chip (on the same 2.5D interposer), which greatly shortens the data transmission path and reduces signal latency.
- Power Efficiency: Due to the ultra-wide bus width and short transmission distance, HBM's energy consumption per bit for equivalent bandwidth is far lower than GDDR or traditional DDR, achieving outstanding power efficiency.
Commercial Landscape and Procurement Guide (Ecosystem and Procurement)
Market Landscape: Three Giants and Technology Roadmaps
The HBM market is currently dominated by three major memory giants, each with a different focus in their technology roadmap and mass production schedule:
- SK Hynix: Pioneer and leader in the HBM field, often the first to achieve large-scale mass production of new generations (such as HBM3).
- Samsung (Samsung): Leveraging its strong DRAM manufacturing capabilities, it closely follows in HBM capacity and integration technology, with ventures into innovative areas like HBM-PIM.
- Micron (Micron): Demonstrates strong competitiveness in high-speed versions like HBM3e and is committed to delivering highly energy-efficient products.
Call to Action / External Link TrustCompo Electronic specializes in providing you with the latest High Bandwidth Memory solutions. For details and technical specifications on Micron and Samsung's newest HBM product lines, please contact our professional consultants.
Key Parameters for HBM Procurement
To ensure optimal performance for AI servers and accelerators, customers should focus on the following key parameters when purchasing HBM:
| Parameter | Description | Impact on AI Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Generation | HBM3 vs HBM3e (or future HBM4) | Most critical. Determines the fundamental performance ceiling and power efficiency. |
| Capacity (Stack Size) | GB per stack (e.g., 8Hi/12Hi) | Determines the scale of the model that can be loaded (e.g., LLM parameter count). |
| Total Bandwidth (TB/s) | Bandwidth of the entire system (sum of all stacks) | Directly determines the data throughput rate for AI training and inference. |
| Power Consumption (W/GB/s) | Energy consumption required per GB/s of bandwidth | Affects thermal design and data center operating costs. |
| Lead Time | Time from order to delivery | Market is tight, supply stability is a critical business consideration. |
HBM Selection Recommendations: For top-tier AI training, prioritize HBM3e and higher generations; for cost-sensitive inference or smaller models, HBM3 may be considered. Always match the number and capacity of HBM stacks to the target AI accelerator's maximum supported capacity and system bandwidth requirements.
Procurement Case Study: LLM Accelerator Selection Guide
One of our clients (an AI startup) plans to procure a batch of AI accelerators to train a Large Language Model (LLM) with 175 billion parameters. They require a single accelerator card to have enough local memory to hold model weights and activation values, and provide at least 1.0 TB/s of bandwidth to meet high-speed training needs.
| Requirement Metric | Target Value | Traditional Memory Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Model Scale (Parameters) | 175B | Model cannot be fully loaded onto a single card with traditional memory (insufficient capacity) |
| Minimum System Bandwidth | 1.0 TB/s | Traditional DDR5/GDDR6X bandwidth cannot meet the speed requirement (insufficient speed) |
Selection Guidance Process:
1. Determine Capacity Requirement:
- A 175 billion parameter model, using FP16 (half-precision float) storage, basic weights occupy: $175 \times 10^9 \times 2 \text{ bytes} \approx 350 \text{ GB}$.
- Considering the gradients, optimizer states (e.g., Adam requires 12x parameter size), and activation values needed during training, single-card memory needs at least 500 GB to train effectively.
- Conclusion: The upper limit of traditional GDDR6X is typically 48GB-96GB, which is insufficient. A high stack layer count (e.g., 12Hi/16Hi) HBM solution must be chosen.
2. Determine Bandwidth Requirement:
- The client requires a minimum of 1.0 TB/s bandwidth.
- Generation Choice: Only HBM3 or HBM3e can achieve this level. HBM2e's bandwidth ceiling is usually around 0.4 TB/s, which is immediately ruled out.
- Option 1 (HBM3): Assuming HBM3 single stack total bandwidth is 0.82 TB/s. At least $1.0 \text{ TB/s} / 0.82 \text{ TB/s} \approx 1.22$ stacks are needed, meaning the accelerator design requires at least 2 HBM3 stacks to meet the bandwidth requirement.
- Option 2 (HBM3e): Assuming HBM3e single stack total bandwidth is 1.2 TB/s. Only 1 HBM3e stack is needed to meet the bandwidth requirement, making the design more efficient.
3. Final Recommendation (Comprehensive Consideration):
Recommended Solution: Select an AI accelerator card integrating multiple HBM3e stacks.
- HBM Generation: Lock in HBM3e to ensure single-card bandwidth reaches or exceeds 1.2 TB/s.
- Total Capacity: Choose a configuration with a total capacity of 96 GB or 128 GB and above (achieved through multiple 8Hi/12Hi stacks) to fully load and efficiently run the model.
- Procurement Consideration: Due to the tight supply of HBM3e, we recommend that the client signs a long-term supply agreement with us and considers working with suppliers who have stable channels with SK Hynix, Samsung, or Micron.
Our real-world case directly illustrates how capacity and bandwidth, the two core HBM parameters, determine the feasibility and efficiency of an AI training task.
Seize the Memory Opportunity of the AI Era
HBM is no longer just a simple DRAM product; it is a critical technology for unleashing the computational power of AI accelerators, and a core solution for overcoming the "I/O Wall" and power consumption challenges. Any enterprise pursuing high-performance AI systems must integrate HBM into its core strategy.
HBM technology will continue to evolve towards higher speeds (e.g., HBM4, projected >10 Gbps/Pin) and higher stack layers (16Hi or more). Concurrently, new 2.5D/3D packaging technologies will continuously improve integration density and power efficiency.
Value Proposition
In the current complex environment where HBM supply is tight, choosing a reliable partner is paramount.
- Professional Service: TrustCompo Electronic possesses a deep technical background and can provide in-depth technical consulting and adaptation services, from HBM generation selection and capacity matching to system integration.
- Supply Guarantee: In the current constrained market, we leverage stable global supply channels and rapid response mechanisms to provide you with more secure HBM procurement solutions.
